
When a computer boots after joining a new Active Directory Domain.Windows 8.1/Server 2012 R2 system or later): The following contains the triggers for foreground synchronous processing on operating systems affected by Group Policy Caching (i.e. There are certain scenarios where Windows will revert to the Windows 2000 foreground synchronous processing. So, why does foreground synchronous processing still exist? This made foreground processing work like background processing – Group Policy processing did not need to be complete to display the logon screen, or the user desktop. When Microsoft introduced Windows XP, the concept of foreground asynchronous processing was introduced. This made the process of booting and logging on to a Group Policy managed computer slow. The desktop was presented only after the full foreground processing was completed for the user. When the computer booted, the logon dialog only displayed after the full foreground Group Policy processing was completed. Back in the ancient days of Windows 2000, every foreground Group Policy interval was synchronous. Every Group Policy processing thereafter is processed in the background. The foreground processing also comes in two flavors, a synchronous and s ynchronous.įoreground Group Policy processing happens when a computer starts, or when a user logs on. There are two main types of processing: foreground and background – both of which exist for User and Computer policies. To further understand the issue, one needs to understand the different flavors of Group Policy processing. Once the GPO hits the clients, any background caching will stop. The actual setting is called Configure Group Policy Caching and it should be set to Disabled. Disabling the feature can be done using Group Policy from:Ĭomputer Configuration\Policies\Administrative Templates\System\Group Policy Our recommendation is to disable caching on clients if dictionaries are being used. These lists, which can be hundreds of megabytes in size, are copied at every Group Policy interval to the computers. This is not an issue from a security perspective, but obviously an unnecessary network operation.


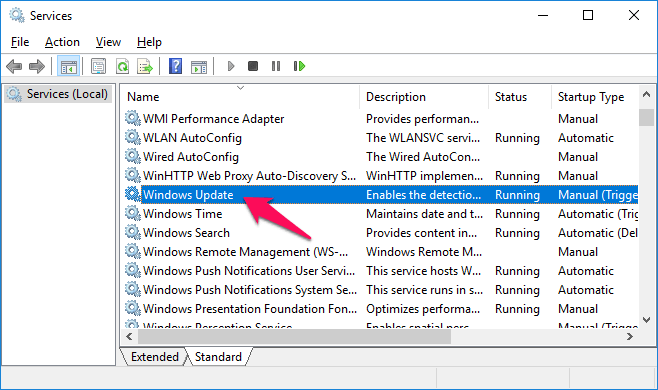
Leaving the Group Policy Caching in its default state will download the password dictionaries and hash lists stored in the Group Policy. Here’s the issue as it relates to Specops Password Policy. Even if no changes have been made to the Group Policy, and no local Group Policy Client Side Extension (CSE) is installed for the settings, the behavior will remain the same. Here’s the drawback: for every Group Policy update interval, Group Policy Caching will download, and store a local copy of all Group Policies that apply to the computer or user. Its purpose is to reduce the time it takes to perform certain scenarios for s ynchronous foreground Group Policy refresh. The release of Windows 8.1 and Server 2012 R2 introduced a new Group Policy concept called Group Policy Caching.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
